The internet can open up a whole new way for us to engage with the world—from staying in touch with family and friends to finding helpful information (or the latest celebrity gossip!). If you're new to computers or you haven’t spent much time online, learning how to navigate a web browser is a great first step.
In this article, we’ll guide you through the basics of browsing the internet to help you explore confidently and safely.
What is a web browser?
A web browser is a software application that allows us to access and explore the internet (in fact, you’re using one right now to view this article). All websites are viewed through a browser “window.” Think of it as your portal to the millions of websites available online. Whether you want to check your email, watch videos, shop, or read the latest news, you’ll use a browser to get there.
Due to its speed and convenience, Google Chrome is the most popular web browser in use today. Other browsers include Apple Safari, Mozilla Firefox, and Microsoft Edge. These all work similarly, but each might look a little different or have different features.
How do I use a web browser?
AT&T has a free online course that you can take at your own pace that covers the basics of navigating your way around websites. But if you want to get started now, below is a simple guide to get you started in exploring online. In this example, we are using the browser Google Chrome.
Step 1: Find you browser icon. On your computer desktop or in the app menu on your smartphone, look for the icon (thumbnail image) of the browser you want to use. For example (see image below), Chrome has a colorful circle logo, Safari shows a compass, and Firefox has an orange fox around a blue globe.

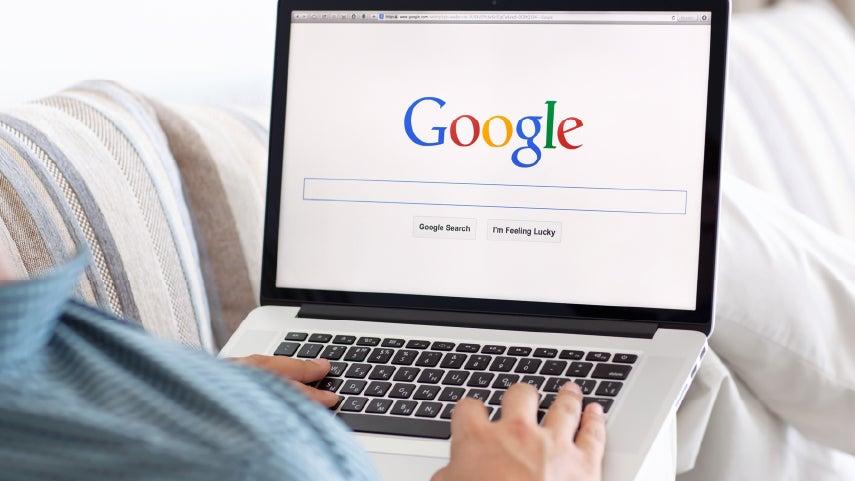
Step 2: Open the browser. Click the browser icon, and it will open a window as shown in the image below. When you open a web browser, you’ll typically see a blank page or a search engine like Google, as is the case in the image above. At the top of the browser window, there’s a bar where you can type in addresses of websites (like www.google.com). This is called the address bar.
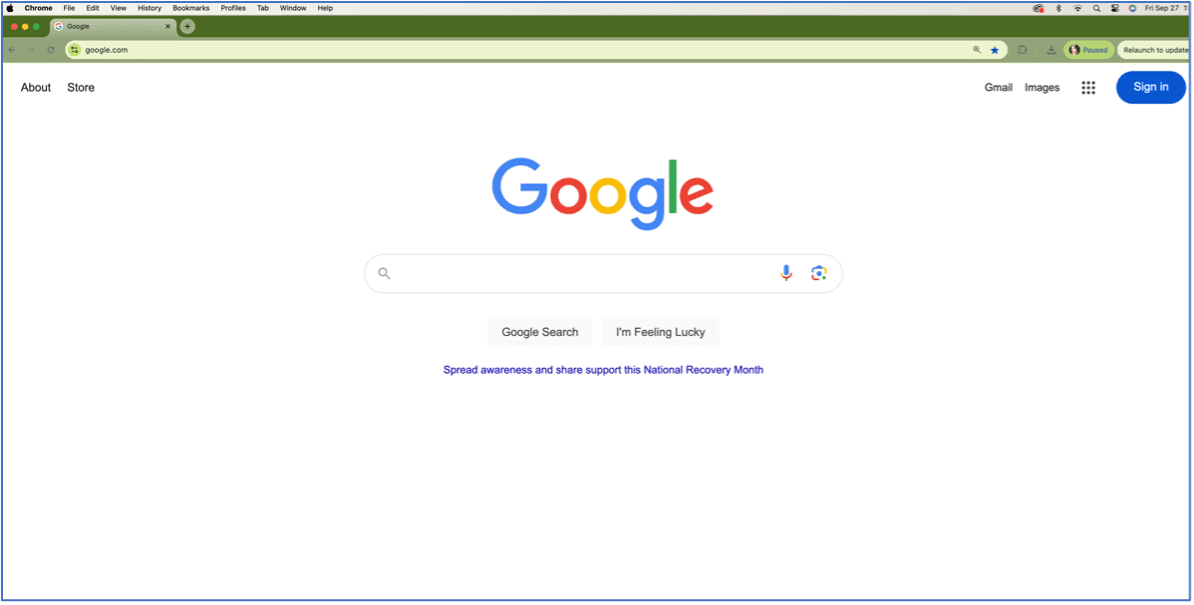
Step 3: Search for information. Once you have the browser open and you’re connected to the internet, you can start exploring. One of the simplest ways to find what you're looking for is by typing keywords into the search field (which may be powered by Google, Bing, or another search engine).
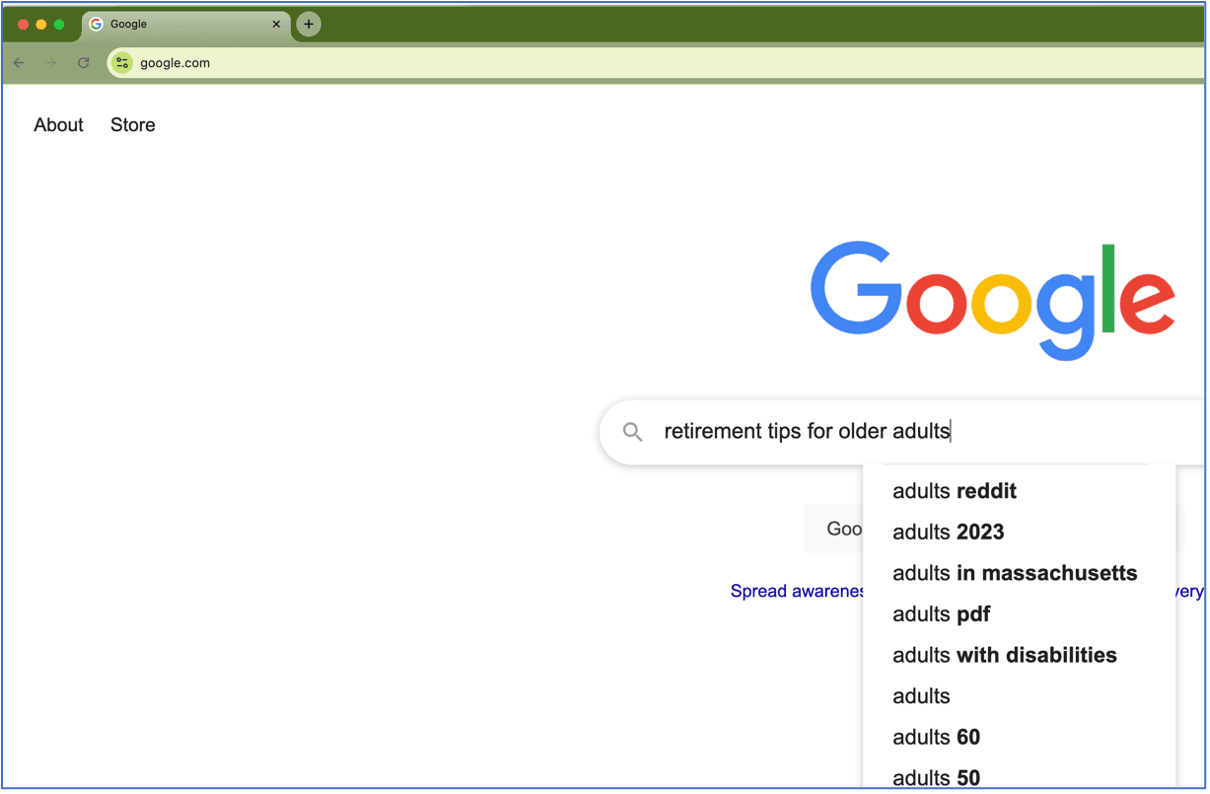
For example, like the image above, if you’re looking for retirement tips for older adults, type “retirement tips for older adults” and hit Enter.
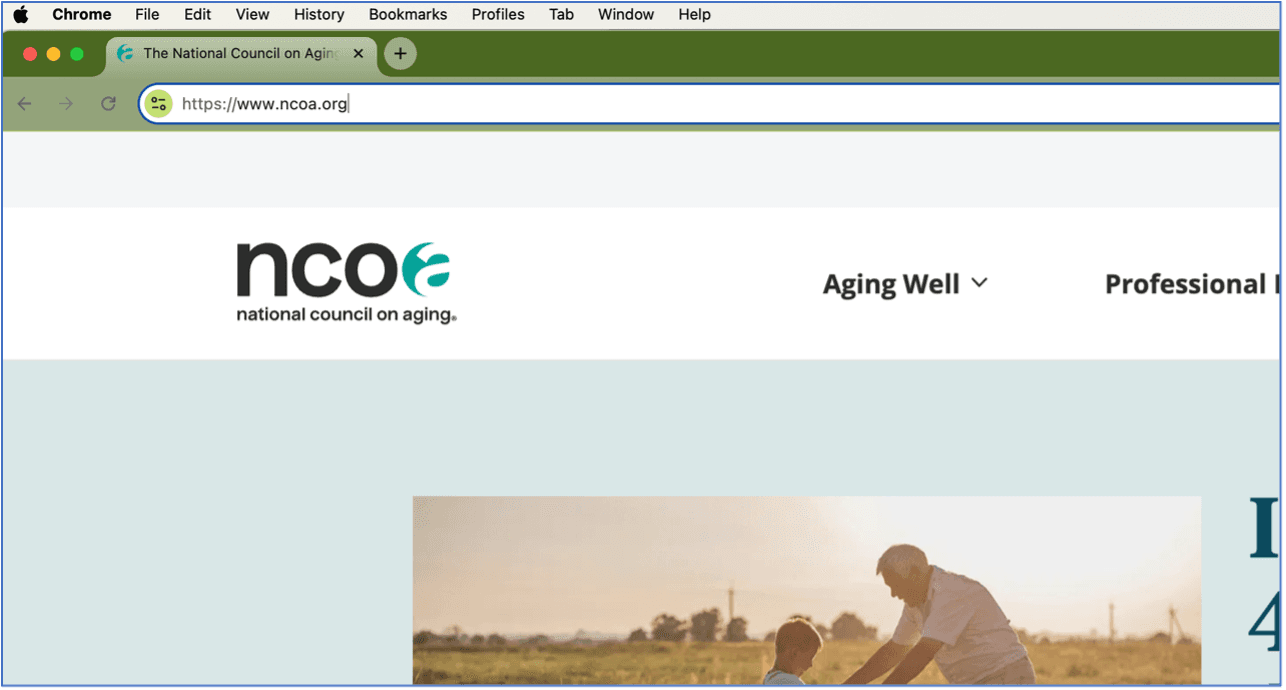
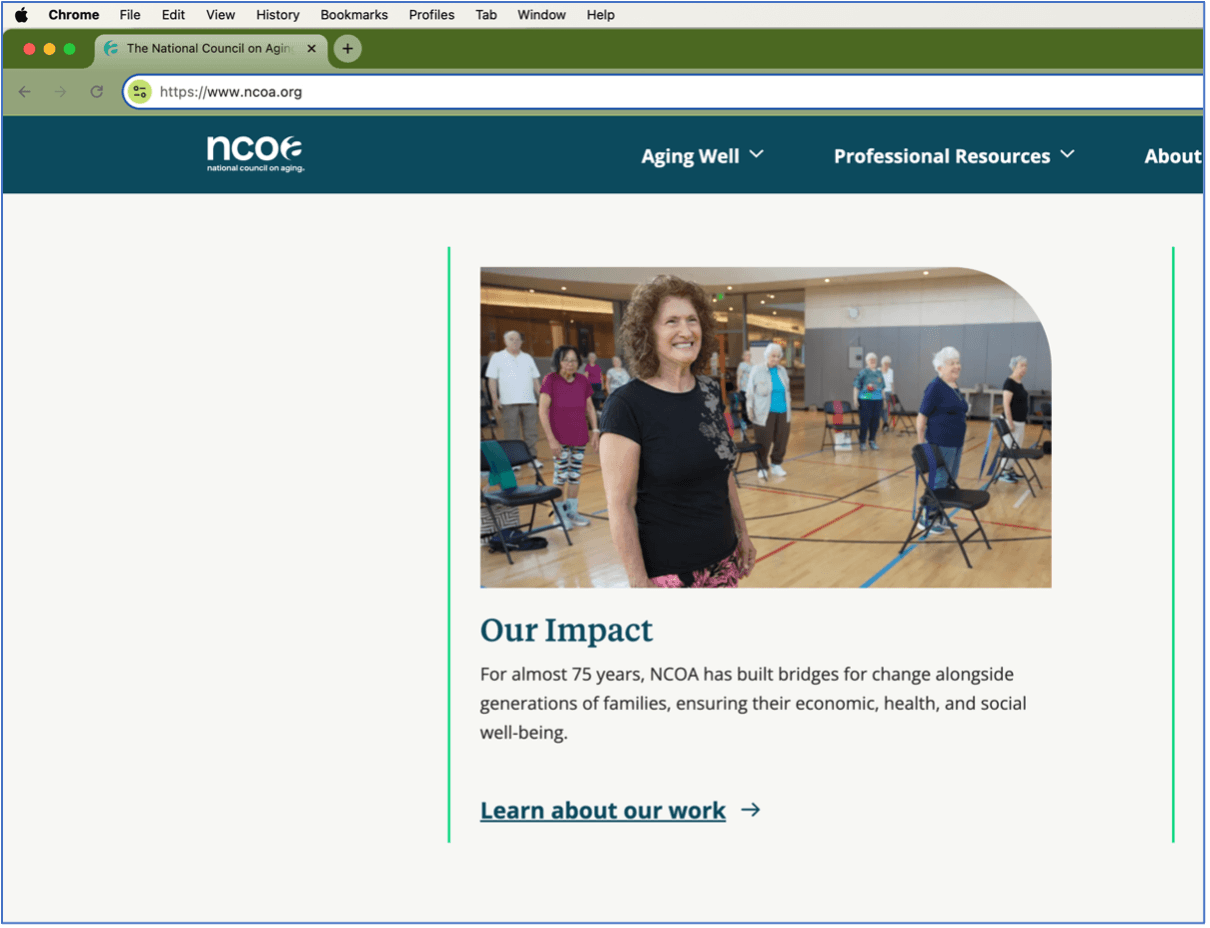
Step 4: Enter a web address. If you already know the website you want to visit, you can type the full address (like www.ncoa.org in the image below) into the address bar at the top of the browser. This will take you directly to that website. Keep in mind that when you open any browser, there will already be a web address in the address bar. To type in a new one, simply click on the address until it’s highlighted. Then, you can either just start typing over the existing address or hit your Delete key to clear the bar before you begin typing.
Step 5: Click on links that interest you. Websites have links (usually blue text and/or underlined in blue, like 'Learn about our work' in the image below) and buttons you can click to go to another page or section of a website. When you see a link or button you want to follow, just click on it, and the browser will load the new page.
What are the different features of a web browser?
Web browsers come with some helpful features to help you manage your browsing experience. These include:
- Tabs: At the top of the browser window, you’ll see a "+" symbol. Clicking this opens a new tab, which lets you visit another website without closing the one you're currently on. Tabs allow you to have multiple sites open at once in one browser window—instead of cluttering up your screen with several browser windows.
- Back and forward buttons: These buttons, usually at the top left of your browser window, let you go back to the page you were on previously or move forward again. This feature is useful when you’ve clicked a link but want to return to the original page.
- Bookmarks: Did you find a website you want to return to later? Bookmark it! In Google Chrome, you’ll find a small star on the right side of the address bar. Clicking it will save the website to your bookmarks, so you don’t have to type in the address again to visit it in the future. To see and visit your bookedmarked pages, click on “Bookmarks” in the Google Chrome menu at the very top of your screen.
- Refresh button: Sometimes, web pages don’t load correctly. You can click the refresh button to reload the page. In Chrome, the refresh icon is a circular arrow at the left of the address bar.
- Browser history: The web browser history feature records the websites and pages you visit, including website addresses (URLs) and timestamps (when you last visited). You can use the history feature to track your browsing activity and revisit sites. Your history can be viewed, searched, or cleared for privacy.
- Security: Web browsers come with built-in security features designed to protect you from online threats. These features include warnings for unsafe or malicious websites, pop-up blocking, and prevention of tracking by unscrupulous sites and entities.
- Download manager: If you want to download something from the internet, such as a document or a photo, clicking a download link will usually bring up a prompt to save the file on your computer or phone. You can find all the files you’ve downloaded by clicking “Window” and then “Downloads” in your top Chrome menu.
- Extensions: Web browser extensions are small software programs that can be added to your browser to enhance its functionality. Extensions can add features such as ad blocking, password management, language translation, and productivity tools. Grammarly, for example, is a popular browser extension that reviews your spelling, grammar, punctuation and more as you type and offers corrective suggestions.
What are some web browser safety tips?
While using a browser is simple, there are a few safety tips to keep in mind to avoid scams and other threats while exploring the web:
- Use only secure websites: Make sure any websites you visit begin with “https://” (not “http://”) to ensure a secure connection.
- Avoid clicking on suspicious links: Be careful of unfamiliar links. Emails, text messages, and social media posts can all contain malicious links from scammers out to steal your personal information (and your money). Signs of suspicious links include use of hyphens and symbols, URLs that contain all numbers, and URLs shortened with services like Bitly or TinyURL.
- Be wary of pop-ups: Even if they appear to be from recognizable organizations, don’t respond to or click on pop-up windows on your phone or computer. Criminals often rely on "scareware" to deceive older adults. This type of scam uses "urgent" pop-up security alerts and other tricks to pressure you into downloading or buying bogus software disguised as legitimate cybersecurity protection. Learn more about financial scams targeting older adults.
- Limit your use of public networks: Don't perform personal transactions while using a public network (e.g., a WiFi network at your local coffee shop). These are unsecured networks that make it risky to check your personal medical records online or do online banking. It's best to wait on these activities until you get home.
- Keep your browser updated: Most browsers update automatically, but it’s important to have the latest version to stay protected from security threats. Many browsers, such as Chrome, update automatically when you close and then reopen your browser. However, you can also check for updates manually by clicking the three dots in the top right corner of your browser, selecting "Help," then "About Google Chrome," and then "Update Google Chrome."
Are there courses online that can help me navigate a website?
If you want to be more confident browsing websites, start with AT&T's free course. AT&T Connected Learning℠ also offers other free courses that you can take at your own pace, including learning how to use a PC (Windows 10) to searching for information online. Find more online courses to gain confidence and improve your tech skills today.